Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems are critical for modern diesel vehicles to meet strict emission standards. With the latest Snap-on® Diagnostic Software release, technicians now have access to new special functions for Mercedes diesel vehicles (2017 onwards) equipped with AdBlue®. These functions simplify the diagnosis and repair of SCR issues, including AdBlue dosing, sensor calibration, and system resets.
This article explores how the SCR system operates, common causes for SCR issues, and demonstrates practical workflows using real-world examples to diagnose and repair SCR issues.
How SCR Systems Work
The SCR system reduces harmful NOx emissions by injecting AdBlue® (Urea / Diesel Exhaust Fluid) into the exhaust system. Key components include:
- NOx sensors – measure nitrogen oxide levels before and after the SCR catalyst
- AdBlue injector – delivers precise dosing to the exhaust
- Selective Catalytic Reduction module – converts NOx into nitrogen and water
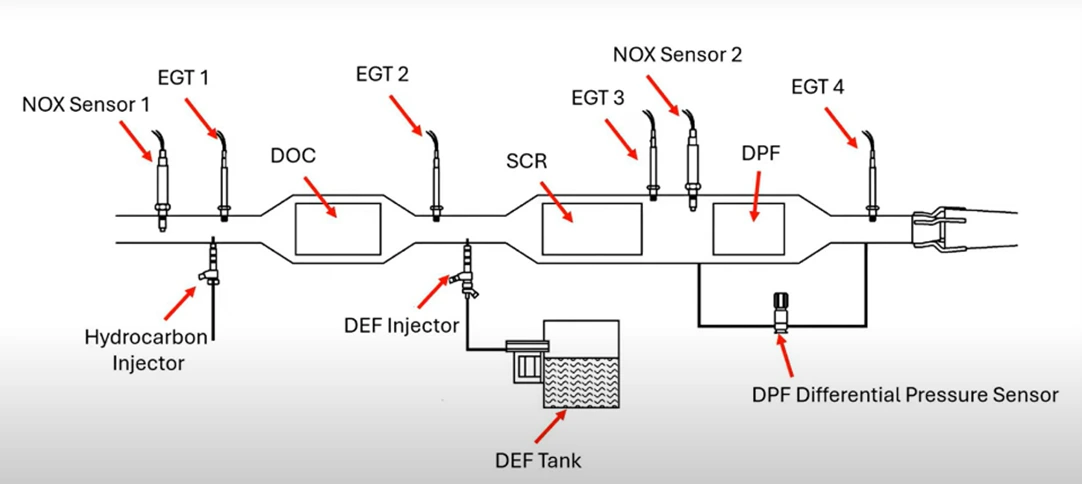
Diesel Emission System Workflow
Typical diesel emission systems follow this sequence:
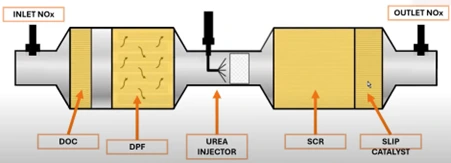
DPF → Urea Injector → SCR → Slip Catalyst
Snap-on® Diagnostic Software allows technicians to monitor and test each stage:
- DPF status and regeneration: Static or dynamic regen procedures, teach-in for replaced filters, and soot load verification.
- SCR functional checks: Urea dosing, visual leak tests, injector and pump actuation.
- Sensor verification: Confirm upstream/downstream NOx and ammonia sensors using scan data and optional tailpipe measurement.
Why SCR Issues Occur
- Leaks in pipework (visual leak test available in special functions)
- Poor quality AdBlue®
- EGR circuit failure
- Ignored AdBlue tank refill warnings (vehicle will not start if the tank is empty)
- High mileage causing excessive oil consumption
Common DTCs include:
- P20EE – NOx Catalytic System Efficiency below threshold
- P20E6 or P20E8 – Reductant injection pressure too low
Understanding NOx and Ammonia Sensors
NOx sensors are central to emission control, measuring oxides of Nitrogen at both the inlet and outlet of the SCR system. While highly effective, conventional NOx sensors can misidentify ammonia as NOx, leading to falsely elevated readings. Some manufacturers incorporate additional ammonia sensors to improve accuracy and prevent interference from other exhaust gases.
Key points for technicians:
- Inlet and outlet NOx readings indicate SCR effectiveness.
- Ammonia sensors serve as a backup to prevent false NOx readings.
- Cross-checking scan tool data with a 5-gas or single-gas analyser ensures reliable measurements.
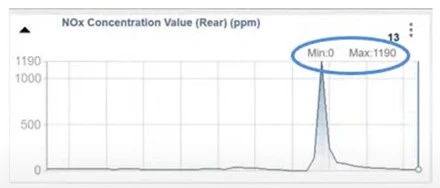
- Normal operation: 300 ppm in, 30 ppm out (~90% reduction)
- Total failure: 300 ppm in, 300 ppm out
- Partial failure: Intermediate readings indicate sensor or SCR malfunction

Snap-on (HHGA5CP) Hand Held 5 Gas Analyzer Kit with Printer
AdBlue® / SCR Testing
SCR systems require precise dosing of AdBlue® to convert NOx into harmless nitrogen and water. Functional tests include:
- Triggering dosing events to check spray patterns and flow.
- Verifying tank level, heater operation, and pressure.
- Cross-referencing NOx sensor feedback for accurate SCR efficiency checks.
SCR Special Functional Tests
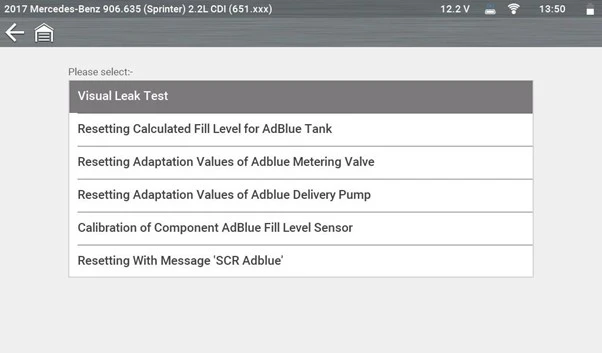
The latest software introduces advanced Special Functions for SCR systems, taking the stress out of diagnosing and repairing AdBlue® system issues. These include:
- Teach-In Process
- Calibration of Component (AdBlue Fill Level Sensor)
- Resetting the Calculated Fill Level of AdBlue Tank
- Resetting Learned Values of AdBlue Tank Component
- AdBlue Pressure Line Heating Element Activation
- AdBlue Tank Heating Element Activation
- Evacuation of System Pressure Line
- Bleeding of System
If a fault develops with the heater element, AdBlue pump, or level sensor, the complete tank must be replaced. These special functions eliminate the guesswork and provide guided support to take the stress away from diagnosing and repairing these SCR issues entering your workshop.
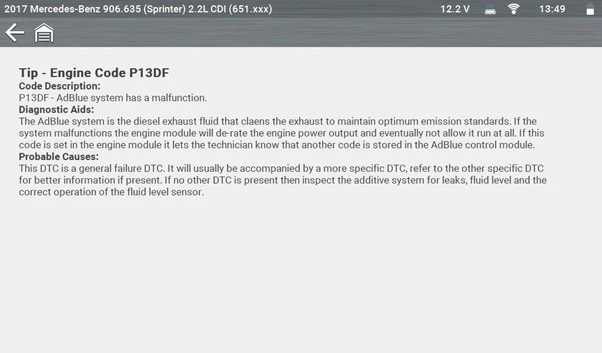
Case Study: 2017 Mercedes Sprinter – Diagnostic Trouble Code P13DF-00
Complaint
A 2016 Mercedes Sprinter 2.2 Diesel was recovered to a workshop with a no-start condition. The garage owner observed that the instrument cluster displayed an AdBlue® range of zero miles, preventing the vehicle from starting. The van had been used by multiple drivers, none of whom had acted on the AdBlue countdown warnings.
A Pre-Scan was performed, revealing numerous DTCs across several modules. Of particular interest was P13DF-00 – AdBlue system malfunction, general failure.
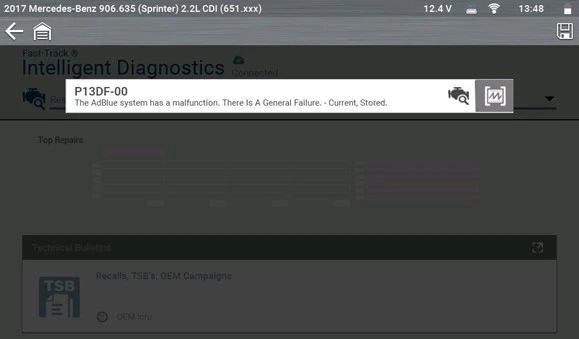
Cause
Using Fast-Track® Intelligent Diagnostics, no top-repair graph results were found, but a Technical Service Bulletin (TSB) from Mercedes was available for reference.



Additional guidance within Troubleshooter provided enhanced information on the fault code.
Live data indicated the AdBlue tank level at 0.00 litres – completely empty.
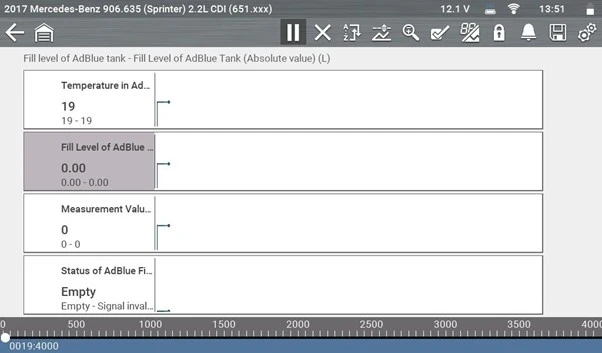
After adding 5 litres of quality-tested AdBlue® (verified at 32.5 % urea concentration using a refractometer), the level reading increased slightly, though not by the full 5 litres expected.
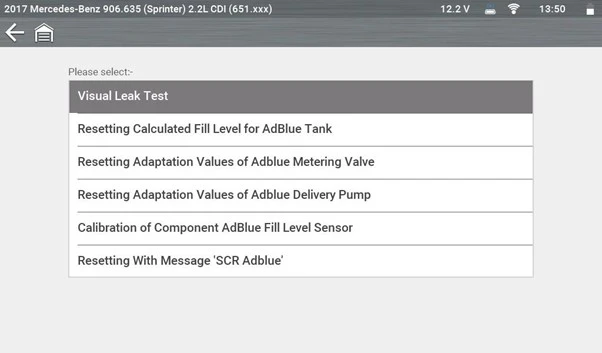
To confirm system integrity, a Visual Leak Test was performed via the special functions menu. The line should have pressurised to around 5 bar, but minimal pressure was achieved.
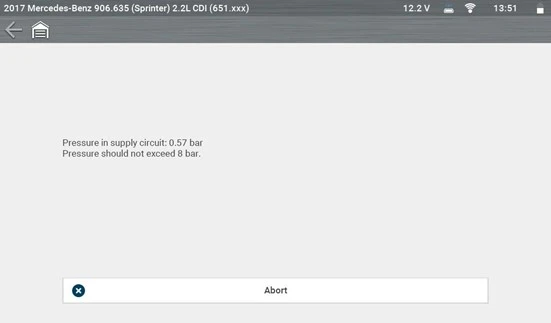
A manual pressure-gauge check at the injector supply line confirmed 0 bar. Power and ground signals were verified at the reductant pump using the Snap-on® Information System wiring diagram and integrated test plan. Despite correct voltage and ground, the pump failed to actuate, even after a light tap of ‘percussive persuasion’.
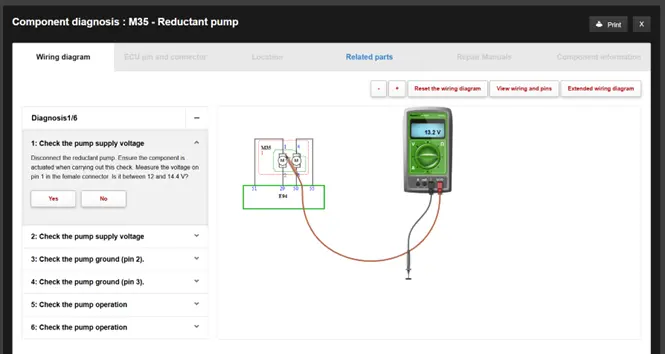
The investigation determined that the AdBlue pump had failed due to the tank being run completely dry, leading to internal damage.
Correction
The workshop opted to replace the AdBlue tank assembly, which includes the pump and level sender.
Once fitted and filled with new AdBlue®, the technician used Snap-on® special functions to:
1. Recalculate the tank fill level
2. Run delivery-pump adaptation
3. Calibrate the level sensor
4. Reset the SCR AdBlue® warning message
Following these steps, the ‘0 miles to no start’ message cleared, and the van started successfully.
The MIL remained illuminated initially due to other stored engine ECU codes, which were subsequently addressed. After final verification, the vehicle operated fault-free, with no warnings or codes present.
Extended Coverage Across Mercedes Diesel Platforms
The diagnostic workflow demonstrated in this 2017 Mercedes Sprinter case study applies to a wide range of Mercedes-Benz diesel vehicles equipped with AdBlue®. The same special functions—such as AdBlue® fill level recalibration, component teach-in, pressure line bleeding, and SCR warning resets—follow an identical structure across other supported models.
With the latest Snap-on® Diagnostic Software release, this SCR coverage now extends to include:
- C-Class (206) – 2020–2025
- E-Class (214) – 2024–2025
- S-Class (223) – 2021–2025
- GLC-Class (254) – 2023–2025
These additions ensure technicians can confidently carry out accurate diagnostics, maintenance, and repairs across the full Mercedes-Benz diesel range—whether working on light commercial vehicles or the latest passenger car platforms.
With full SCR system coverage now available, workshops can expect consistent diagnostic performance, guided procedures, and verified repair confidence on every supported Mercedes diesel vehicle.
Through a structured diagnostic approach using Fast-Track® Intelligent Diagnostics and Snap-on® special functions, the technician identified a failed AdBlue® pump caused by an empty tank. Guided procedures enabled efficient recalibration and reset after component replacement, restoring full SCR functionality and resolving the no-start issue.
Supporting Visuals & Reference Links
Internal Article: Mastering Diesel Functional Tests with Snap-on® Diagnostic Software
Diagnostic Live Training: Diesel Emissions Systems Operation and Testing with Jason Gabrenas
Quick Tip: Mercedes-Benz® DEF Level Sensor Relearn
Conclusion
Snap-on® Diagnostic Software’s latest release simplifies SCR system diagnostics for Mercedes diesel vehicles, from AdBlue® tank calibration to NOx sensor verification. These special functions reduce guesswork, streamline repairs, and ensure compliance with emission standards.
Ensure your workshop is on the latest Snap-on® software release to access exclusive SCR special functions, guided workflows, and diagnostic efficiency.
FAQ’s
- Can I perform these SCR special functions on older Mercedes diesel vehicles?
A: Coverage applies to 2017 diesel vehicles onwards. Extended vehicle support includes C-Class (206), E-Class (214), S-Class (223), and GLC-Class (254).
- What happens if the AdBlue pump or heater fails?
A: If the pump, heater element, or level sensor fails, the complete AdBlue tank must be replaced.
- How do I verify NOx sensor accuracy?
A: Cross-check inlet and outlet readings using the scan tool and confirm with a 5-gas or single-gas analyser.
- Can these special functions prevent “no-start” conditions?
A: Yes. Resetting tank fill levels and calibrating sensors ensures the vehicle recognises AdBlue levels, preventing engine immobilisation.